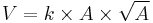Tetrahedral hypothesis
The Tetrahedral hypothesis is an obsolete scientific theory attempting to explain the arrangement of the Earth's continents and oceans by referring to the geometry of a tetrahedron. Although it was a historically interesting theory in the late 19th and early 20th century, it was superseded by the concepts of continental drift and modern plate tectonics.
Contents |
Theory
This idea, described as ‘"ingenious" by geologist Arthur Holmes,[1] is now of historical interest only. It attempted to explain apparent anomalies in the distribution of land and water on the Earth's surface:[2]
- More than 75% of the Earth's land area is in the northern hemisphere.
- Continents are roughly triangular.
- Oceans are roughly triangular.
- The north pole is surrounded by water, the south pole by land.
- Exactly opposite the Earth from land is almost always water.
- The Pacific Ocean occupies about one third of the Earth's surface.
To understand its appeal, consider the "regular solids": the sphere and the 5-member set of Platonic Solids. The solid with the lowest number of sides is the tetrahedron (four equilateral triangles); progressing through the cube, and the icosahedron (20 sides), the sphere can be considered to have an infinite number of sides. All six regular solids share many symmetries.
Now, for each regular solid, we may relate its surface area and volume by the equation:
where k is a characteristic of each solid, V its volume, and A its area. As we traverse the set in order of increasing number of faces, we find that k increases for each member; it is 0.0227 for a tetrahedron and 0.0940 for a sphere. Thus the tetrahedron is the regular solid with the largest surface area for a given volume, and makes a reasonable endpoint for a shrinking spherical Earth.[3]
History
The theory was first proposed by William Lowthian Green in 1875.[4] It was still popular in 1917 when summarized as:
"The law of least action … demands that the somewhat rigid crustal portion of the earth keep in contact with the lessening interior with the least possible readjustment of its surface. … a shrinking sphere tends by the law of least action to collapse into a tetrahedron, or a tetra-hedroid, a sphere marked by four equal and equidistant triangular projections; and the earth with its three about equal and equidistant double continental masses triangular southward with three intervening depressed oceans triangular northward, its northern ocean and southern continent, with land everywhere antipodal to water, realizes the tetrahedroid status remarkably.“[5]
This is suggesting that a cooling spherical Earth might have shrunk to form a tetrahedron, with its vertices and edges forming the continents, and four oceans (Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean and Arctic Ocean) on its faces.
By 1915 German Alfred Wegener (1880–1930) had proposed in his continental drift theory that land masses moved great distances over the Earth's history. Wegener was also at first met with hostile reactions.[6] By the mid 1920s the same Holmes developed theories on what could cause the drift.[7][8] The plate tectonics theory is now generally accepted to explain the dynamic nature of the Earth's surface; the tetrahedral shape plays no special role in modern theories.[9] Explanations of details such as water to land ratios, the precise shape of continents and their sizes continue to be developed.
References
- ^ Arthur Holmes (1965). Principles of physical geology. Nelson. p. 32. ISBN 0174480202. http://books.google.com/books?id=XUJRAAAAMAAJ.
- ^ A. Z. Bukhari (2005). "Continental Drift". Encyclopedia of nature of geography. Anmol Publications PVT. Limited. pp. 109–113. ISBN 9788126124435. http://books.google.com/books?id=vef_5GExuUgC&pg=PA109.
- ^ Principles of Physical Geography. APH Publishing. 2004. pp. 84–85. ISBN 9788176487313. http://books.google.com/?id=TXkdMyGF_wgC&pg=PA84&lpg=PA84.
- ^ William Lowthian Green (1875). Vestiges of the molten globe, as exhibited in the figure of the earth, volcanic action and physiography. London: E. Stanford. OCLC 3571917. http://books.google.com/books?id=9DkDAAAAQAAJ.
- ^ Benjamin Kendall Emerson (1917). "Tetrahedral Deformations and Intercontinental Torsions". Proceedings, American Philosophical Society (American Philosophical Society) 56 (6): pp. 445–472. ISBN 9781422372531. http://books.google.com/books?id=4lULAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA445.
- ^ "Alfred Wegener (1880-1930)". University of California Museum of Paleontology web site. University of California. 2006. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/wegener.html. Retrieved August 4, 2010.
- ^ Arthur Holmes (June 6, 1925). "The Origin of the Continents". Nature 115 (2901): 873–874. doi:10.1038/115873a0.
- ^ Arthur Holmes (September 22, 1928). "Theory of Continental Drift: a Symposium on the Origin and Movement of Land Masses, both Inter-Continental and Intra-Continental, as proposed by Alfred Wegener". Nature 122 (3073): 431–433. doi:10.1038/122431a0.
- ^ "Plate Tectonics: The Rocky History of an Idea". University of California Museum of Paleontology web site. University of California. 2006. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/geology/techist.html. Retrieved August 4, 2010.
Further reading
- Edna Kenton. The Tetrahedral Earth. Forgotten Books. ISBN 9781605064154. http://www.sacred-texts.com/earth/boe/boe34.htm. Retrieved August 4, 2010.